
That frequency shift is directly related to the motion of the raindrops. The reflected radar signal is measured by the radar's receiver with a change in frequency. For example, a Doppler radar transmits a signal that gets reflected off raindrops within a storm. Radar can measure precipitation size, quantity, speed and direction of movement, within about 100 mile radius of its location.ĭoppler radar is a specific type of radar that uses the Doppler effect to gather velocity data from the particles that are being measured. Part of this beam of energy bounces back and is measured by the radar, providing information about the object. The radar transmits a focused pulse of microwave energy (yup, just like a microwave oven or a cell phone, but stronger) at an object, most likely a cloud.
Radars emit microwave energy, a longer wavelength, highlighted in yellow. Working together, engineers, technicians, and scientists collectively design, develop and operate the advanced technology of radars that are used to study the atmosphere.ĭoppler weather radars are remote sensing instruments and are capable of detecting particle type (rain, snow, hail, insects, etc), intensity, and motion. Radar data can be used to determine the structure of storms and to help with predicting severity of storms.Įnergy is emitted in various frequencies and wavelengths from large wavelength radio waves to shorter wavelength gamma rays.
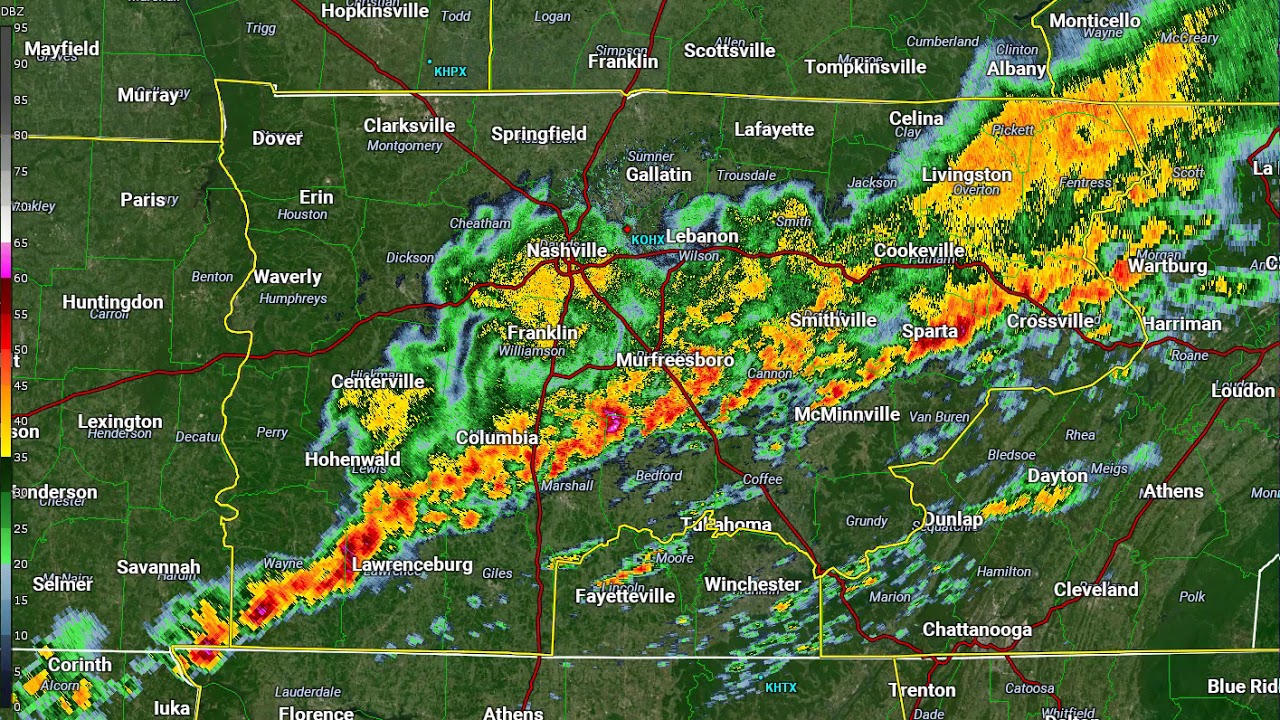
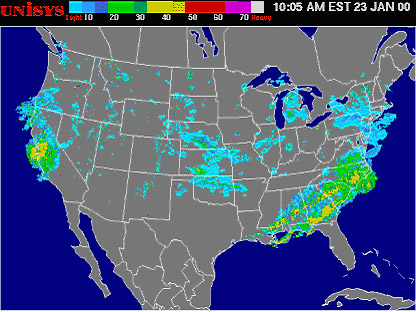
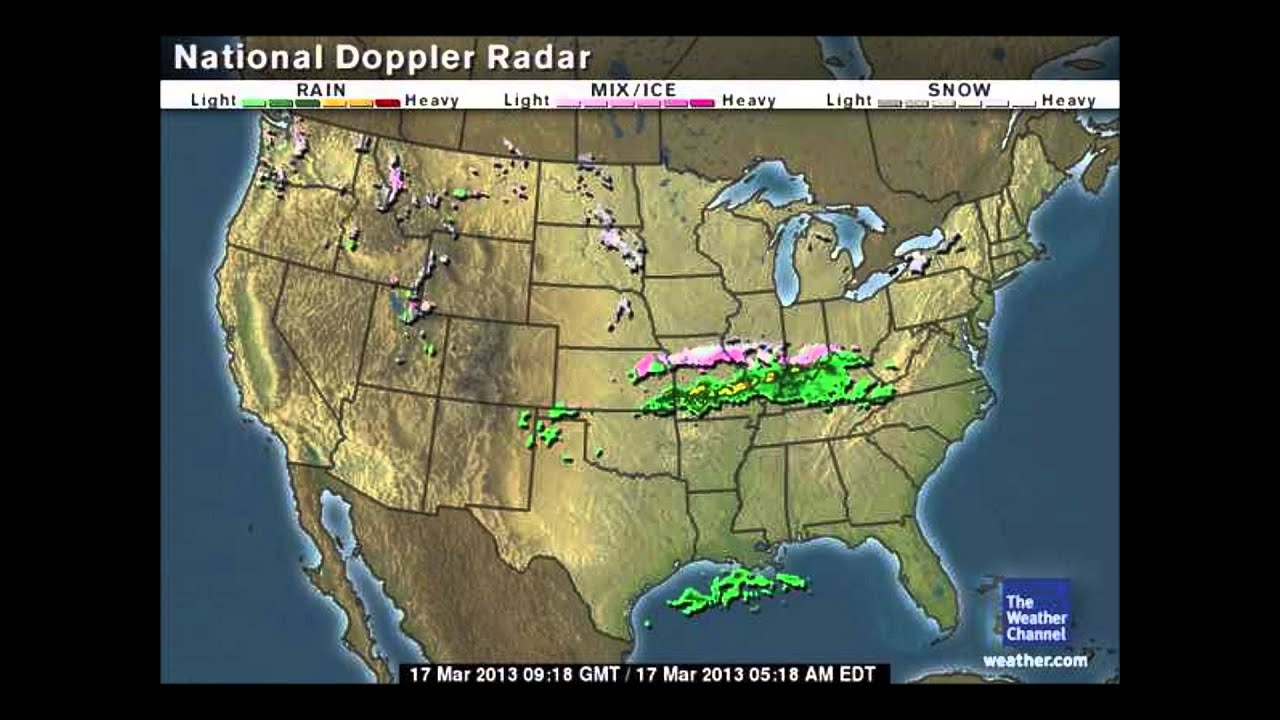
Radars are critical for understanding the weather they allow us to “see” inside clouds and help us to observe what is really happening.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
